Layout Algorithms
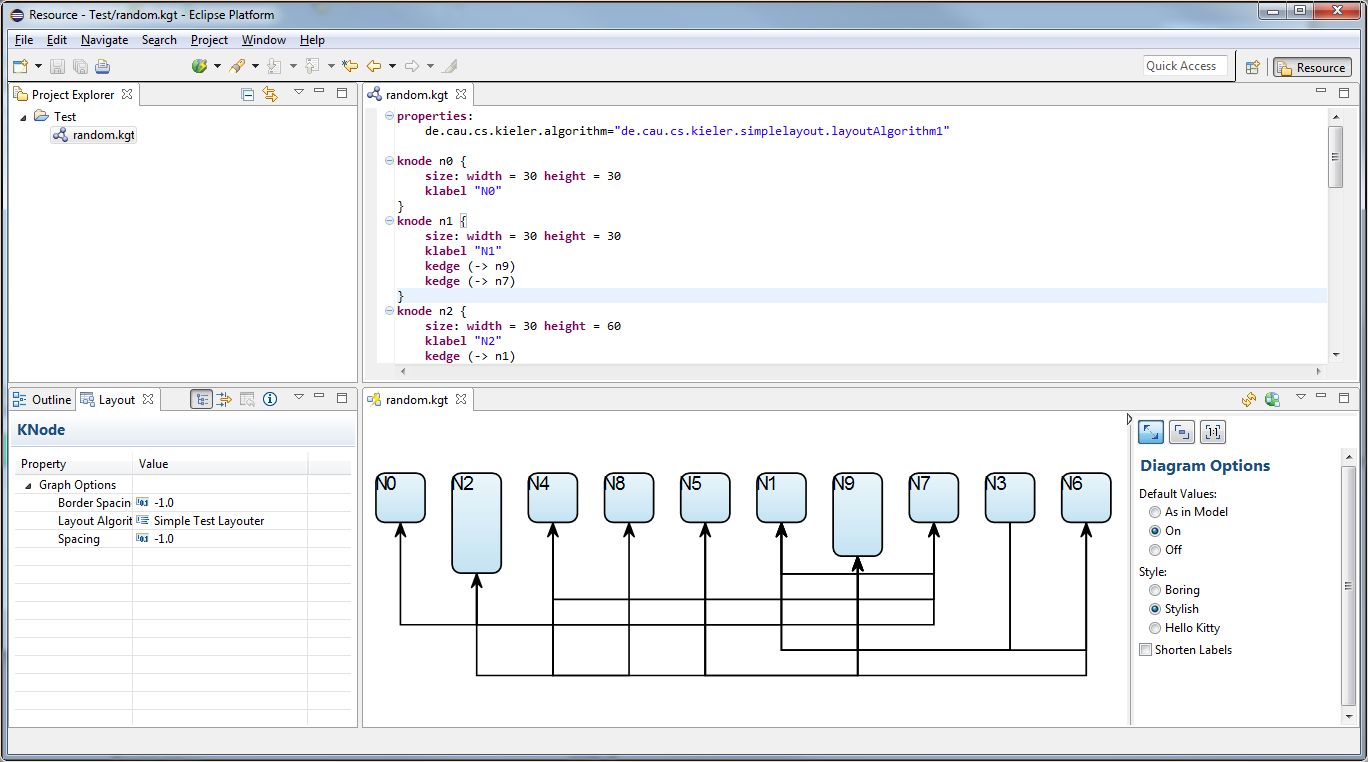
Welcome to this tutorial! We will work our way through installing a proper Eclipse setup and developing a first very basic layout algorithm. The layout algorithm will integrate with ELK (Eclipse Layout Kernel), our very own framework that connects graphical editors with layout algorithms. Once you're finished, you should be able to write layout algorithms for ELK. And you should have a running Eclipse-based application that should look something like this:
Preliminaries
There's a few things to do before we dive into the tutorial itself. For example, to do Eclipse programming, you will have to get your hands on an Eclipse installation first. Read through the following sections to get ready for the tutorial tasks.
Required Software
Installing Eclipse for Layout Development
Finding Documentation
Developing Your First Layout Algorithm
Now that the preliminaries are out of the way, it's time to develop your first layout algorithm! It will, however, be a very simple one. This tutorial focuses on creating Eclipse plug-ins and on learning how to develop with ELK.
Adding a New Plug-in
We need to create a new plug-in to implement the layout algorithm in. Switch back to the Java or Plug-in Development perspective and follow these steps:
- Click File > New > Other... > Plug-in Development > Plug-in Project.
- Enter de.cau.cs.kieler.simplelayout as the project name. Click Next.
- Set the execution environment to JavaSE-1.8. (do this for all plug-ins that you create!)
- Uncheck all checkboxes in the Options group and click Finish.
- If Eclipse asks you whether the Plug-in Development perspective should be opened, choose either Yes or No. It doesn't make much of a difference anyway.
Writing the Layout Algorithm
When writing our layout algorithm, we are going to need to be able to access code defined in several other plug-ins. To do that, we need to add dependencies to those plug-ins:
- In your new plug-in, open the file META-INF/MANIFEST.MF. The plug-in manifest editor will open. Open its Dependencies tab.
- Add dependencies to the following plug-ins:
- org.eclipse.elk.core
- org.eclipse.elk.graph
- Save the editor.
Layout algorithms interface with ELK by means of a layout provider class that has to be created and registered with KIML.
- Right-click the source folder of your plug-in and click New > Class.
- Set the package to de.cau.cs.kieler.simplelayout, enter SimpleLayoutProvider as the class name, and select org.eclipse.elk.core.AbstractLayoutProvider as the superclass. (This will only be available through the Browse dialog if you have saved the plug-in manifest editor; if you haven't, Eclipse won't know about the new dependencies yet.)
- Select Generate comments and click Finish.
Implement the layout provider class:
Add the following constants:
/** default value for spacing between nodes. */
private static final float DEFAULT_SPACING = 15.0f;Use the following code as the skeleton of the layout(...) method:
progressMonitor.begin("Simple layouter", 1);
KShapeLayout parentLayout = layoutGraph.getData(KShapeLayout.class);
float objectSpacing = parentLayout.getProperty(CoreOptions.SPACING_NODE);
if (objectSpacing < 0) {
objectSpacing = DEFAULT_SPACING;
}
float borderSpacing = parentLayout.getProperty(CoreOptions.SPACING_BORDER);
if (borderSpacing < 0) {
borderSpacing = DEFAULT_SPACING;
}
// TODO: Insert actual layout code.
progressMonitor.done();- Press CTRL+SHIFT+O or select Source > Organize Imports from the context menu to add all required imports.
- It is now time to write the code that places the nodes.Your code should place them next to each other in a row, as seen in the screenshot at the beginning of the tutorial.
Before you can test your layout code, you will have to register your new layout provider with ELK.
- Right-click the de.cau.cs.kieler.simplelayout package and select New > File.
- Create a file simple.elkm and double click it to open it.
- When asked whether you want to add the Xtext nature, select yes.
The file is used to specify meta information for your layout algorithm. For this, copy the following code snippet into your editor:
package de.cau.cs.kieler.simplelayout
bundle {
label "Simple Layout Algoritms"
metadataClass SimpleMetaDataProvider
}
algorithm simple(SimpleLayoutProvider) {
label "Simple Test Layouter"
metadataClass SimpleOptions
supports org.eclipse.elk.spacing.border
supports org.eclipse.elk.spacing.node
}- You still have to register the file with Eclipse. Open the META-INF/MANIFEST.MF file again and switch to the Extensions tab.
- Add an extension for org.eclipse.elk.core.layoutProviders.
- Right-click the extension and click New > provider.
- Set the class to your bundle's meta data provider class name (use the browse button and enter SimpleMetaDataProvider). Note that SimpleMetaDataProvider is automatically generated from the .elkm file you created. Its name is specified by the metadataClass keyword in the bundle section. What is also created is the SimpleOptions class, which contains everything you need to access layout options from within your layout algorithm.
- Save the editor
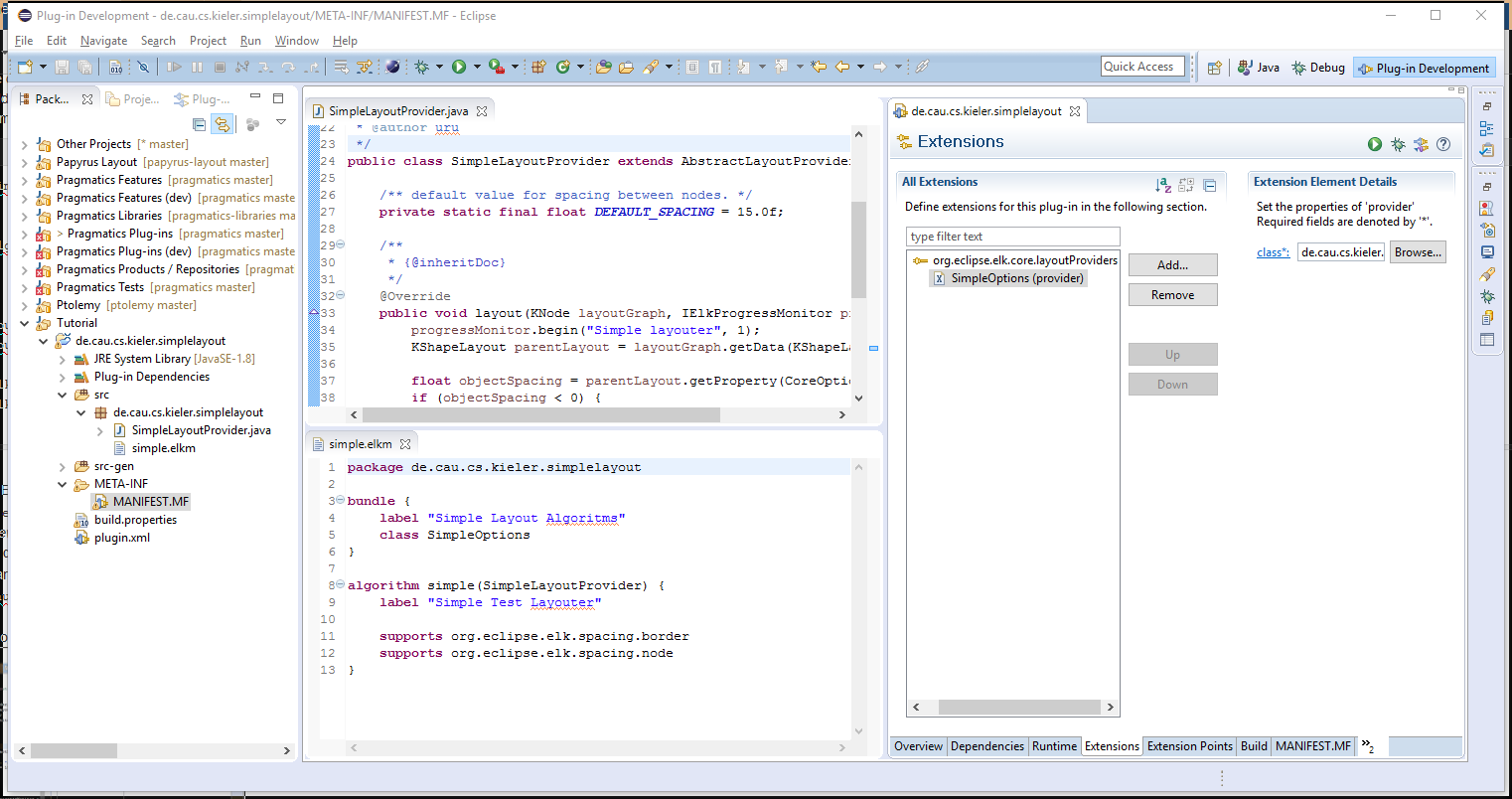
- Your workspace should look similar to this
We will now have to add a new run configuration that will start an Eclipse instance with your layout code loaded into the application, ready to be used.
- Click Run > Debug Configurations...
- Right-click Eclipse Application and click New. Set the configuration's name to Layout Test.
- In the Arguments tab, make sure the the program arguments include -debug and -consoleLog.
- On the Plug-ins tab, set Launch with to plug-ins selected below only.
- Click Deselect All.
- Check the Workspace item in the tree.
- Check the following plugins under Target Platform are checked:
- de.cau.cs.kieler.kgraph.text.ui
- de.cau.cs.kieler.klighd.xtext
- org.eclipse.ui.ide.application
org.eclipse.platform
- Click Add Required Plug-ins. Press it twice (just to be sure!).
- Click Apply to save your changes and then Debug to start an Eclipse instance to test with.
Test the layouter in your new Eclipse instance:
- Click New > Project... > General > Project and set the project name to something like Test.
- Right-click the new project and click New > Other > KGraph > Random KGraph. Enter a meaningful name and click Finish.
- Open the .kgt file. To show up the Diagram vie, select Window > Show View > Other... > Other > Diagram
- Open the Layout view through Window > Show View > Other... > Eclipse Diagram Layout > Layout. Move the view somewhere such that you can see the view and the diagram simultaneously.
- Chose your Simple Test Layouter in the Layout Algorithm section of the Layout View. (If the Layout View shows no properties, click the white background in the Diagram View once.)
- You should see something similar to this
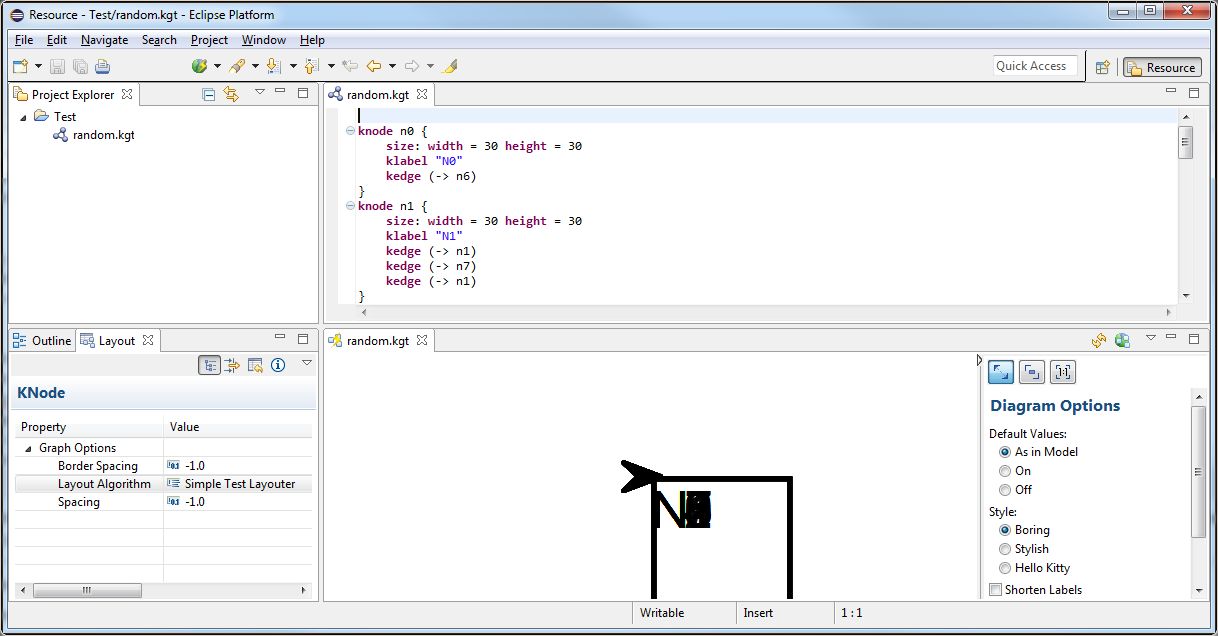
Once you're satisfied with your node placement code, it's time to take care of edge routing.
Add a new method that will implement the edge routing using the following skeleton code:
/**
* Routes the edges connecting the nodes in the given graph.
*
* @param parentNode the graph whose edges to route.
* @param yStart y coordinate of the start of the edge routing area.
* @param objectSpacing the object spacing.
* @return height used for edge routing.
*/
private float routeEdges(final KNode parentNode, final float yStart, final float objectSpacing) {
// TODO: Implement edge routing
return 0;
}- Add a call to routeEdges(...) in your doLayout(...) method and implement the latter.
Once you're done implementing the edge routing code, test it by running your debug configuration again, as before.